7 - SD Zones
7.1 - SD Zones Definition
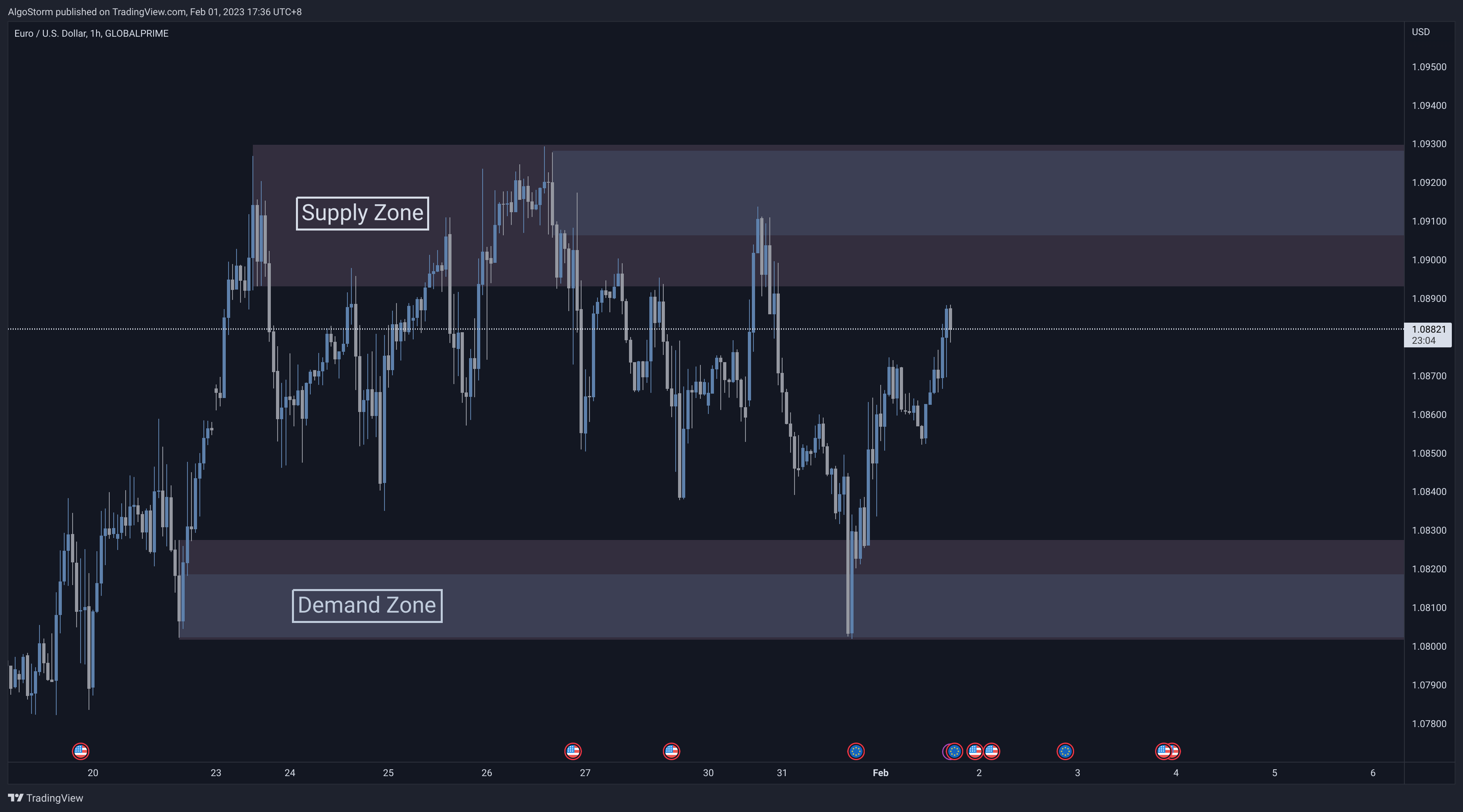
- SD stands for supply and demand zones.
- SD zones are defined when an imbalance in the buyers and sellers occurs.
- SD zones show the origins of price moves and indicate potential institutional trading.
- SD zones form either when banks or institutions have taken profits off or when they place orders into the market.
- SD zones are usually seen as an area of consolidation that comes before an impulsive move.
- The impulsive move must break the market structure for the SD zone to be considered valid.
- The price action often returns to the SD zones that form at the beginning of reversals.
- If a supply or demand zone is going to cause a reversal upon being hit, the market must return to the zone quickly. How quickly it must return is dependent on the time frame in which the supply or demand zone has formed on. For zones on the 1-hour chart, the market must return to the zone within 64 hours of it being created. For zones on the daily chart, the market revisits the zone within 60 days of its creation.
- Old supply and demand zones do not cause reversals to take place in the market. The only time they do this is when the zone is found inside a higher time-frame zone.
- Generally, SD zones that are created from a base (consolidation phase) are more powerful than those created from a single candle.
- SD zones are marked from the high to the low of the range before the start of the move.
- SD zones are used for both entries and exits.
7.2 - SD Zones Price Patterns
| SD Zone Price Pattern | Abbreviation | Description | Reason For Creation | Success Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drop-Base-Drop | DBD | Creates Supply Zone | Profit-Taking | Low Probability |
| Rally-Base-Rally | RBR | Creates Demand Zone | Profit-Taking | Low Probability |
| Rally-Base-Drop | RBD | Creates Supply Zone | Profit-Taking or Placing Orders | Acceptable Probability |
| Drop-Base-Rally | DBR | Creates Demand Zone | Profit-Taking or Placing Orders | Acceptable Probability |